| Description: | A group of organic compounds that contain a macrocyclic lactone ring linked glycosidically to one or more sugar moieties. | ||
| Mechanism of action: | Binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome and inhibiting translocation of peptidyl-tRNA from the A site to the P site. The result of this inhibition is that bacteria are not able to complete proteins that are essential for life. Macrolides are bacteriostatic. | ||
| Source: | |||
| Tylosin | Streptomyces fradiae | ||
|
Tilmicosin |
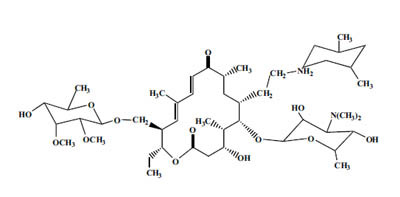
Produced semisynthetically by chemical modifications of desmycosin. | ||
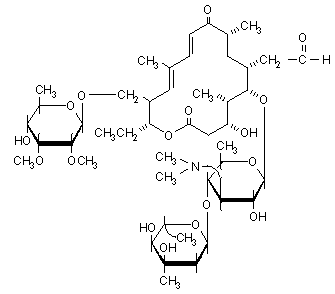
| Chemistry: | Tylosin consists primarily of tylosin factor A with small amounts of three minor factors, desmycosin (factor B), macrocin (factor C) and relomycin (factor D). Tylosin factor A has the highest microbiological potency. | ||
Indications: Mycoplasmosis, Necrotic enteritis, Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale.
| Dosage: |
Chickens:
|
Turkeys:
|
Pigeons:
|
|
Tylosin
|
50 mg/Kg
|
50 mg/kg
|
25mg/kg IM SID; 50mg/kg PO SID*
|
|
Tilmicosin
|
20 mg/kg
|
20 mg/kg
|
ND
|
*SID= Once daily
| Drug interactions: | Florfenicol and lincosamides have mechanisms of action similar to the macrolides; they may be prevented from binding, or prevent a macrolide from binding to the 50 S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. | ||
| Residues |
Tylosin: Residue in tissues is very rare. It is eliminated from the body upon withdrawal of the drug. Eggs: Persistent macrolide residues can be deposited in eggs following oral administration to laying hens. 3 days. Tilmicosin: Liver should be the target tissue for tilmicosin residues in broiler chickens. The recommended withdrawal time is 10 days. |
||
| Pharmacokinetics: |
Protein binding: chickens - 30%
|
||||||||||||
|
TYLOSIN |
|||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
TILMICOSIN |
|||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Tilmicosin is rapidly absorbed and slowly eliminated after oral administration. | |||||||||||||
Comments: Tylosin is considered to be highly lipid soluble. The tartrate salt is soluble in water. The injectable form of the drug (as the base) is in a 50% propylene glycol solution. Tilmicosin has a stronger antimicrobial activity than tylosin against G. anatis, P. multocida and Mycoplasma.






