The fluoroquinolones are synthetic, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents with bactericidal activity. They exert their effects by binding to and inhibiting bacterial DNA-gyrase. This enzyme produces supercoiling of cellular DNA which is needed for bacterial DNA synthesis.
Description: The fluoroquinolones are broad-spectrum antibacterial agents with in vitro activity against many gram-negative and gram-positive organisms.
Mechanism of action: Quinolones rapidly inhibit DNA synthesis by promoting cleavage of bacterial DNA in the DNA-enzyme complexes of DNA gyrase and type IV topoisomerase, resulting in rapid bacterial death. As a general rule, gram-negative bacterial activity correlates with inhibition of DNA gyrase, and gram-positive bacterial activity corresponds with inhibition of DNA type IV topoisomerase.
Indications: Salmonellosis, Colibacillosis, Fowl cholera, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (enrofloxacin)
| Dosage: |
Chickens:
|
Turkeys:
|
Pigeons:
|
|
Enrofloxacin
|
12.5 mg/kg
|
12.5 mg/kg
|
15 mg/kg
|
|
Danofloxacin
|
- |
6 mg/kg
|
-
|
|
Flumequine
|
18-20 mg/kg
|
-
|
-
|
|
Norfloxacin
|
15 mg/kg
|
- | - |
|
Difloxacin
|
10 mg/kg
|
- | - |
Drug interactions: Various drug-drug interactions can occur with the use of the quinolones. Absorption of the quinolones is significantly diminished with the concomitant use of compounds that contain multivalent metal cations such as aluminum, magnesium, zinc, iron, and calcium.
Residues: When given orally or by IM injection to laying hens, fluoroquinolone residues appear in eggs around 24 h after the first dose and persist in both yolk and albumen for several days after cessation of treatment.
Pharmacokinetics:
FLUMEQUINE
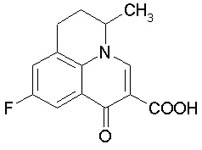
| Animal Species |
Mg/kg
|
Tmax
(Hr) |
t 1/2
(Hr) |
F(%) |
| Pigeons | 10 IM | ~2 | 1.44±0.33 | 22±9 |
| 60 IM | ~4 | 1.69±0.12 | 23±9 | |
| 60 IM | ~2 | 1.57±0.33 | 6.7±2.5 |
|
Animal Species |
Mg/Kg |
Tmax |
t1/2 |
F(%) |
|
Chickens |
5 |
2.50±0.86 |
--- |
80.1 |
|
10 |
1.64±0.04 |
14.23±0.46 |
64.0±0.2 |
|
|
|
6-7 |
59.6 |
||
|
|
4.29 |
80 |
||
|
0.119 |
5.81 |
89.2 |
||
|
4.3 ± 1.98 |
19.51 ± 2.60 |
|
||
|
20 |
4.4 ± 1.58 |
18.77 ± 4.11 |
|
|
|
Turkeys |
10 |
4-6 |
|
|
|
Muscovy Duck |
10 |
1.38±0.18 |
68 |
|
|
Pigeons |
10-15 |
2.6-4.7 |
87-92 |
|
|
African grey parrot |
5-15 |
2-3 |
51 |
|
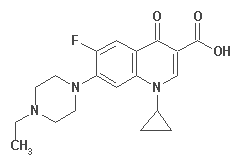
NORFLOXACIN
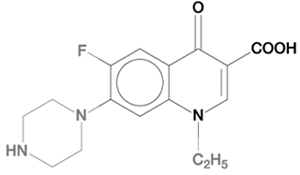
|
Animal
Species |
Mg/kg
PO |
Tmax
(Hr) |
t 1/2
(Hr) |
F(%)
|
| Chickens | 8 | 0.22±0.02 | 12.8±0.59 | 57.0±2.4 |
| 10 | 1.99±0.17 | 11.11±2.28 | ||
| Turkeys | 10 | 1.94±0.08 | 9.07±1.00 | |
| 40 | 0.7 | |||
|
Geese
|
10 | 2.39±0.18 | 10.65±2.41 |
DANOFLOXACIN
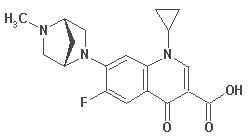
| Animal Species |
Mg/kg
PO |
Tmax
(Hr) |
t 1/2
(Hr) |
F(%)
|
| Chickens* |
5
|
0.50±0.01
|
6.98±0.18
|
100
|
|
1.5
|
6.62
|
99.2
|
||
| Turkeys |
6
|
2.13±2.56
|
9.74±2.93
|
78.37±17.35%
|
* Different studies
DIFLOXACIN
| Animal Species |
Mg/kg
PO |
Tmax
(Hr) |
t 1/2
(Hr) |
F (%)
|
| Chickens |
5
|
1.4
|
7.35
|
86.9
|




